Galvanized steel (GI steel) is a cornerstone material for modern construction, fabrication and a variety of industrial applications. Often supplied in coils and sheets, galvanized steel is known for its superior durability and corrosion resistance, and has become the preferred choice for projects that require a long-lasting, reliable material.
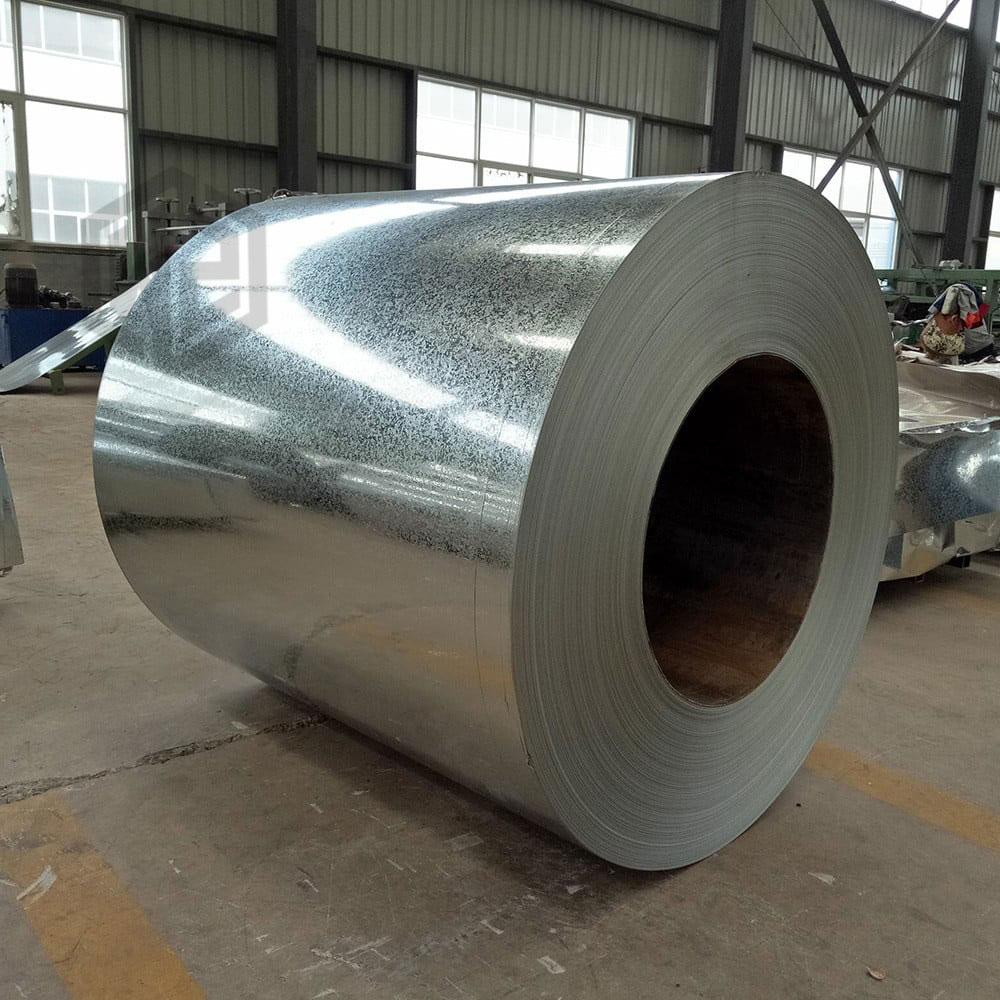

What is Galvanized Steel?
Galvanized steel is a metal-coated steel that is coated with a layer of zinc by hot-dip galvanizing or electro-galvanizing to prevent corrosion and thus extend the service life of the steel. Galvanized steel consists of a substrate and a zinc layer, which acts as a sacrificial anode, i.e. the zinc layer corrodes before the steel below it, and the thickness of the zinc layer determines the corrosion resistance of the steel and the processing.
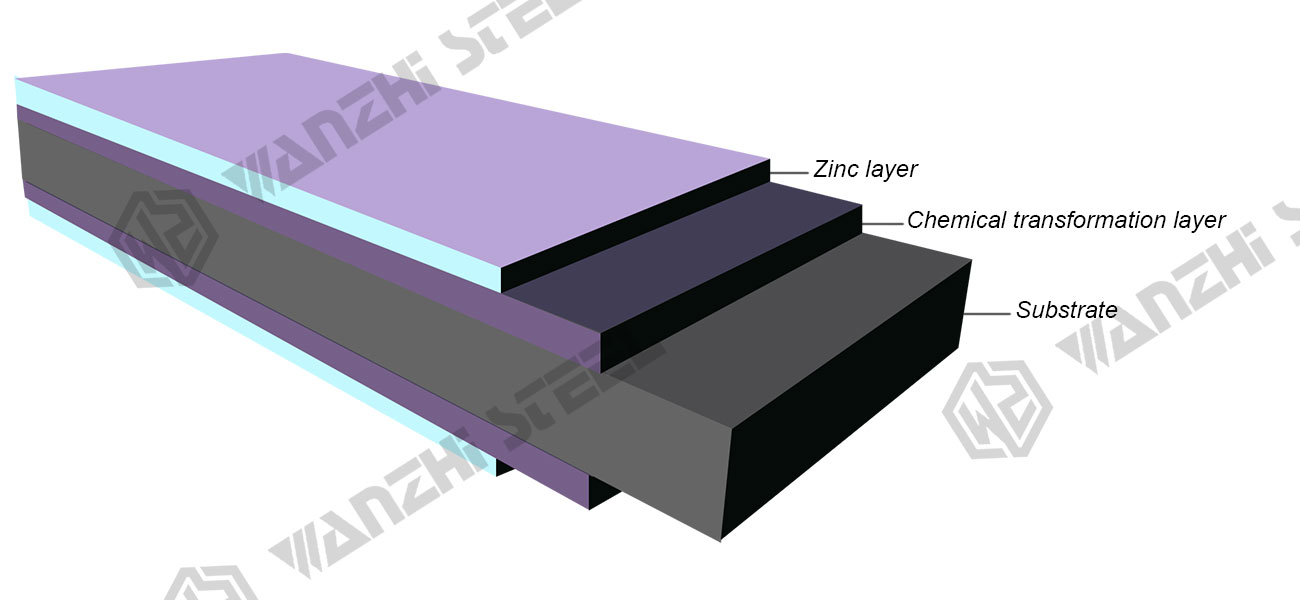
Substrate Types
The substrate for galvanized steel is usually low carbon steel (e.g., cold-rolled or hot-rolled steel sheet), and common substrates include:
- Mild Steel (Mild Steel): carbon content ≤ 0.25%, for general use.
- High Strength Low Alloy Steel (HSLA): trace alloying elements (e.g. Nb, V, Ti) are added to increase strength.
- Ultra-low carbon steel (IF steel): carbon content ≤ 0.005%, used for deep-drawn molding.
According to the strength grade, galvanized steel can be divided into general purpose, stamping, deep drawing, ultra-deep drawing, and so on.
- DX51D (general purpose), DX52D (for stamping), DX53D (for deep drawing), DX54D (for ultra-deep drawing).
- S220GD, S350GD (the number indicates the minimum yield strength, such as 220MPa, 350MPa).
Mechanical properties of substrates
European Standard (EN 10346) Continuous hot-dip galvanized steel sheet/strip
| Grade | Yield strength (MPa) | Tensile strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Main applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DX51D | 140~280 | 270~500 | ≥22 | General molding (construction, household appliances) |
| DX52D | 140~260 | 270~420 | ≥24 | Slightly stamped (higher molding properties are required) |
| DX53D | 120~240 | 270~420 | ≥26 | Deep-drawn molding (complex-shaped parts) |
| DX54D | 120~220 | 270~380 | ≥30 | Ultra deep-drawing (automotive, precision parts) |
Japanese Standard (JIS G3302) Galvanized Steel
SGCC (hot-dip galvanized) and SECC (electro galvanized) have similar mechanical properties, but electro galvanized is more uniformly coated and is suitable for occasions with high surface requirements.
| Grade | Yield strength (MPa) | Tensile strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Type of coating | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SGCC | ≥140 | 270~500 | ≥18 | Hot-dip galvanized | General purpose (roofing, piping) |
| SECC | ≥140 | 270~500 | ≥18 | Electro-galvanized | Electronic product shells, precision parts |
Chinese standard (GB/T 700) Carbon steel
| Grade | Yield strength (MPa) | Tensile strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q195 | ≥195 | 315~430 | ≥33 | Low-strength structural parts, welded pipes |
| Q235 | ≥235 | 375~500 | ≥26 | General-purpose structural steel (construction, machinery) |
Typical chemical composition (substrate)
| Element | Content (%) | Function |
|---|---|---|
| C | ≤0.12 (low carbon) | Affects formability and weldability |
| Mn | 0.20~0.60 | Improves strength |
| P | ≤0.04 | Improves strength but increases brittleness |
| S | ≤0.03 | Reduces toughness (sulfide formation) |
| Si | ≤0.03 (IF steel) | Controls deoxidation |
| Al | 0.02~0.05 | Deoxidizing agent, refines grain size |
Zinc Layer Grade Classification
- Conventional Galvanized: Z60 (60g/m²), Z80 (80g/m²), Z120 (120g/m²), etc.
- High plating: Z180, Z275 (for harsh corrosive environments).
Coating characteristics
- Thickness of coating: usually 40-150 µm, corresponding to a zinc layer weight of 20-350 g/m².
- Coating structure: pure zinc (Zn) or zinc-iron alloy (Z/ZF).
International standard for galvanized steel
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO 3575 | Standard for galvanizing cold rolled mild steel substrates |
| ISO 1461 | Specification for hot-dip galvanized coating (for structural components) |
| ASTM A653/A653M | North American standard for galvanized steel (e.g. CS Type B, FS Type A) |
| EN 10346 | European standard for continuous hot-dip galvanized steel strip (covering the DX series) |
| JIS G3302 | Japanese standard for galvanized steel sheets (e.g. SGCC, SGCH) |
What is Galvanization?
The principle behind galvanization is straightforward yet ingenious. Zinc, a reactive metal, forms a protective layer when exposed to the atmosphere. This layer, primarily composed of zinc carbonate, is highly resistant to corrosion. When steel is coated with zinc, the zinc layer acts as a barrier, preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the underlying steel. Even if the zinc coating is scratched or damaged, the zinc will still protect the steel through a process called cathodic protection.


How to Galvanization? – Manufacturing Processes of Galvanized Steel
Wanzhi Group’s commonly used galvanizing processes include hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing
Hot-Dip Galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing is widely used because of its thick zinc layer, low processing cost and high production efficiency.
- Cleaning: The steel is thoroughly cleaned to remove any dirt, grease, or rust. This is typically done through a series of chemical baths, including alkaline cleaners, acidic pickling, and fluxing.
- Pickling: The steel is dipped in an acidic solution, usually hydrochloric or sulfuric acid, to remove any remaining scale and rust.
- Fluxing: The steel is then dipped in a flux solution, typically zinc ammonium chloride, to prevent oxidation before it enters the galvanizing bath.
- Galvanizing: The cleaned and fluxed steel is immersed in a bath of molten zinc at a temperature of around 450°C (842°F). The zinc bonds metallurgically to the steel, forming a series of zinc-iron alloy layers.
- Cooling: After being removed from the zinc bath, the steel is cooled in water or air, solidifying the zinc coating.
Electro-Galvanizing
The surface of electro-galvanized steel is smooth and flat, and the zinc layer is uniform and beautiful. This process is usually used for steel plates and steel wires that require smooth and uniform coatings, and for precision workpiece processing.
- Cleaning: Similar to hot-dip galvanizing, the steel is cleaned to remove impurities.
- Electroplating: The steel is submerged in an electrolyte solution containing zinc ions. An electric current is passed through the solution, causing the zinc ions to deposit onto the steel surface.
- Rinsing and Drying: The steel is rinsed to remove any residual electrolyte and then dried.
Applications of Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel’s salt spray resistance and mechanical properties make it suitable for use in a variety of industries including construction, automotive, appliances, transportation, education, energy, and more.
Construction
In the construction industry, galvanized steel(GI steel coil sheet) is used for structural framing, roofing, siding, and rebar. Its corrosion resistance makes it an ideal choice for buildings and infrastructure exposed to harsh weather conditions.
Automotive
The automotive industry relies on galvanized steel to manufacture body panels, chassis, and undercarriages. The material’s durability and resistance to rust ensure that vehicles remain in good condition for a long time, even in environments with high moisture and salt content.
Agriculture
Galvanized steel is widely used in agricultural fencing, feed troughs, and storage boxes. Its ability to withstand outdoor environments without corroding makes it a practical choice for agricultural equipment and structures.
Infrastructure
GI steel is used to manufacture utility poles, cable trays, and transmission towers. The material’s strength and resistance to environmental factors ensure the reliability and longevity of utility infrastructure.
Education
Galvanized steel as a substrate can be coated with functional coatings to make painted galvanized steel, which can be cut, striped and processed into writing boards, blackboards and other materials widely used in teaching, office, etc.
Household appliances
Many household appliances, such as washing machines, refrigerators and air conditioners, are made of GI steel. The durability and corrosion resistance of this material help to extend the service life of these appliances and improve their performance.
Transportation
High-strength or high-zinc-layer galvanized steel is used in applications such as road facilities (highway guardrails (corrugated beams), traffic sign poles, street light poles), public transportation, etc., taking into account safety, durability and economy, and is an ideal metal material.
Marine
In the marine environment, exposure to salt water will accelerate corrosion, so galvanized steel Z275 is used for hulls, docks and other structures. The high zinc coating provides an additional layer of protection against the corrosive effects of salt water.
Advantages of Galvanized Steel
Galvanized steel combines the mechanical properties of steel with the salt spray resistance of zinc to provide high strength and hardness, corrosion resistance, durability, durability and workability.
Corrosion resistance
The main advantage of galvanized steel is its excellent corrosion resistance (the thicker the zinc coating, the greater the corrosion resistance). The zinc coating acts as a barrier to prevent moisture, oxygen and other corrosive substances from entering the underlying steel and protects the steel from corrosion and rust.
Durability
This Z30-Z275 galvanized steel has a service life of 20-50 years. It can withstand extreme temperatures, humidity and chemicals, making it ideal for outdoor and industrial applications.
Cost-effective
Galvanized steel, especially hot-dipped galvanized steel, is a cost-effective choice due to its low processing costs, long service life and low maintenance costs.
Low Maintenance
Galvanized steel has extremely low maintenance costs compared to other metallic materials. The zinc coating provides long-lasting protection and reduces the need for frequent inspections and repairs.
Environmentally friendly
Zinc is a natural element and is fully recyclable. The galvanizing process produces very little waste, and the zinc coating can be recycled an unlimited number of times without any loss of performance. This makes galvanized steel an environmentally friendly choice.
Aesthetics
Galvanized steel has a unique glossy appearance and is available in zero spangle/ regular, big and small spangle finishes to enhance the aesthetics of structures and products.
Processability
Galvanized steel can be stamped, slit, formed, painted, coated, etc. to suit a variety of applications.
Galvanized Steel Products
Wanzhi Group is a professional supplier of galvanized steel (GI Steel), we have a mature galvanized product line and a full range of galvanized products, including hot-dip galvanized steel coils, galvanized steel sheets/strips, galvanized steel pipes, galvanized steel tubes, galvanized screws and nuts, color-coated galvanized steel and so on, which are used for building, transportation, home appliance, manufacturing and so on.
- Galvanized steel sheets/strips (for construction, automotive, home appliances)
- Galvanized steel pipes (scaffolding, water pipelines)
- Galvanized steel wires/strands (electric power, telecommunication)
- SECC (Electro-galvanized steel sheet) (electronics housings, automotive interiors)
- Galvanized screws/nuts (fasteners)
- Galvannealed zinc-iron alloy steel
- Painted galvanized steel (PPGI/PPGL) (roofing, walls, etc.)
Maintenance Tips for Galvanized Steel
In addition to enhancing the galvanized coating and finish of galvanized steel, regular maintenance can extend the life of galvanized steel.
Regular Cleaning
Regular cleaning of galvanized pipe surfaces with mild soap and water helps maintain the appearance and performance of the steel. Avoid abrasive cleaners or chemicals that may damage the galvanized coating when removing dirt and debris!
Inspect for Damage
Periodically inspect galvanized steel for signs of damage such as scratches or dents. Damage to the surface coating can affect the steel’s resistance to corrosion and cause it to rust. In case of slight deterioration, the galvanized steel can be re-galvanized.
To repair damage
When damage to the galvanized coating is detected, first clean the surface and then apply a zinc-rich coating to the damaged area. This will restore the protective coating and prevent rusting.
Avoid harsh chemicals
Avoid harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that may damage the galvanized coating. If cleaning is necessary, use a mild detergent and a soft cloth or brush.
Monitoring Environmental Conditions
The condition of galvanized steel should be monitored more frequently in environments with high levels of contaminants or salt. If necessary, take additional protective measures, e.g. oiling, laminating, painting, etc.
Galvanized Steel Buying Guide
How to choose the most suitable galvanized steel products?When buying galvanized steel, first look at the environment (corrosion determines the thickness of the coating), then look at the processing (stamping/welding requirements determine the type of substrate), and finally look at the budget (electro-galvanized > hot-dip galvanized > color-coated sheet).
Environment
The thickness of the zinc coating and the process determines the service life of the steel in different applications. Hot-dip galvanized steel has a coating thickness of 40-150 μm and electro-galvanized steel has a coating of 5-20 μm.
Hot-dip galvanizing: This is the most common method of galvanizing, in which the steel is dipped into molten zinc to cover the surface with a layer of zinc. The advantages are a thick layer of zinc, high corrosion resistance and suitability for outdoor environments.
Electro-galvanizing: Zinc is deposited onto the steel surface by electrolysis. It has the advantage of a smooth surface and is usually used for light loads, indoor environments indoor or low corrosion environments.
Processing
Normal bending / stamping: DX51D / SGCC (low cost, basic formability).
Deep Drawing / Complex Molding: DX54D / SECC (High elongation, smooth surface).
Welding Requirements: Galvannealed (Zinc-iron alloy plating, good weldability)
Galvanized Steel Frequently Asked Questions
Electro-galvanized: finer surface, suitable for precision parts (e.g. electronics).
Salt spray test: Standard galvanized (Z120) should be able to pass a 500-hour neutral salt spray test.
Color coated panels (PPGI) have their own organic coating and do not require additional treatment.
EN (European Standard)
GB (Chinese National Standard)
Galvanized steel is a versatile and durable metal material with excellent corrosion resistance and long service life. It is widely used in construction, automobiles, agriculture and home appliances. Whether you are a builder, engineer or factory, Wanzhi galvanized steel can provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for your material needs.
